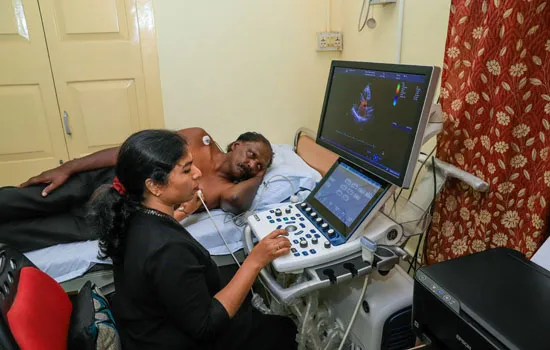
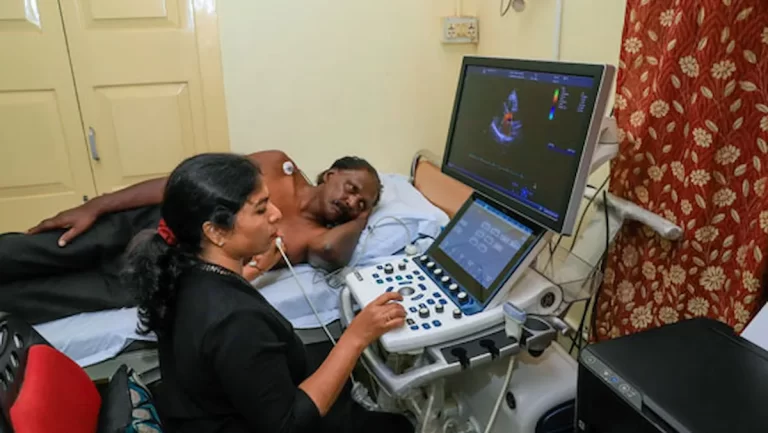
An echocardiogram uses sound waves to produce images of your heart. This common test allows your doctor to see your heart beating and pumping blood. Your doctor can use the images from an echocardiogram to identify heart disease.
Your doctor may suggest an echocardiogram to:
- Check for problems with the valves or chambers of your heart
- Check if heart problems are the cause of symptoms such as shortness of breath or chest pain
- Detect congenital heart defects
- To check the function of your heart
- Assessment of heart before surgery
Transthoracic echocardiogram
In this standard type of echocardiogram:
- Gel is spread on a device (transducer).
- The operator (doctor/sonographer) presses the transducer firmly against your skin, aiming an ultrasound beam through your chest to your heart.
- The transducer records the sound wave echoes from your heart.
- A computer converts the echoes into moving images on a monitor.
Contrast ECHO
If your lungs or ribs block the view, you may need a small amount of an enhancing agent injected through an intravenous (IV) line(Contrast ECHO). The enhancing agent, which is generally safe and well tolerated, will make your heart’s structures show up more clearly on a monitor.Saline (sterile salt water) and Definity are contrast solutions which may be used. Each can show the flow of blood through the heart and enhance the pictures of the heart.
Risks
No risks are involved in a standard transthoracic echocardiogram. You may feel some discomfort from the transducer being held very firmly against your chest. The firmness is necessary to produce the best images of your heart.
Food and medications
No special preparations are necessary for a standard transthoracic echocardiogram. You can eat, drink and take medications as you normally would.
During the procedure
For a standard transthoracic echocardiogram:
- You’ll undress from the waist up and lie on an examination table or bed.
- The technician will attach sticky patches (electrodes) to your body to help detect and conduct your heart’s electrical currents.
- Gel is applied to the transducer that improves the conduction of sound waves.
- The transducer is moved back and forth over your chest to record images of sound-wave echoes from your heart. You may hear a pulsing “whoosh,” which is the ultrasound recording the blood flowing through your heart.
- You may be asked to breathe in a certain way or to roll onto your left side.
Most people can resume their normal daily activities after an echocardiogram.
If your echocardiogram is normal, no further testing may be needed. If the results are concerning, you may be referred to a doctor trained in heart conditions (cardiologist) for more tests.
At Muhil Heart Centre standard 2D ECHO is performed by the cardiologist by a latest and sophisticated machine (GE Vivid S60). The cardiologist is a renowned echocardiographer and has performed more than 50,000 ECHOS thus far.